Osmosis
09.25
Diposting oleh Melany Christy
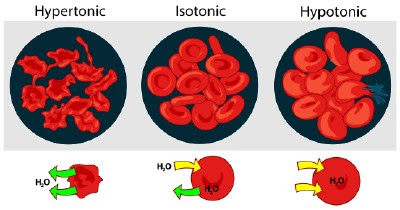
Osmosis is a special case of passive transport. In osmosis water diffuses from a hypotonic (low solute concentrated) solution to a hypertonic (high solute concentrated) solution. Generally speaking, the direction of water flow is determined by the solute concentration and not by the "nature" of the solute molecules themselves. If the blood cells in the image above are placed in salt water solutions of different concentrations, the following will occur:
- If the salt water solution is hypertonic it would contain a higher concentration of solute and a lower concentration of water than the blood cells. Fluid would flow from the area of low solute concentration (the blood cells) to an area of high solute concentration (water solution). As a result the blood cells will shrink.
- If the salt water solution is isotonic it would contain the same concentration of solute as the blood cells. Fluid would flow equally between the blood cells and the water solution. As a result the blood cells will remain the same size.
- If the salt water solution is hypotonic it would contain a lower concentration of solute and a higher concentration of water than the blood cells. Fluid would flow from the area of low solute concentration (water solution) to an area of high solute concentration (the blood cells). As a result the blood cells will swell and even burst.
This entry was posted on October 4, 2009 at 12:14 pm, and is filed under
biology,
Cellular Processes
. Follow any responses to this post through RSS. You can leave a response, or trackback from your own site.
Langganan:
Posting Komentar (Atom)

Posting Komentar