The Nucleus
21.03
Diposting oleh Melany Christy
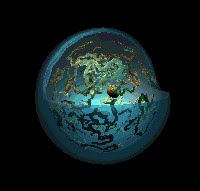 The nucleus is a membrane bound structure that contains the cell's hereditary information and controls the cell's growth and reproduction.
The nucleus is a membrane bound structure that contains the cell's hereditary information and controls the cell's growth and reproduction.
It is commonly the most prominent organelle in the cell.
Distinguishing Characteristics:
The nucleus is bounded by a double membrane called the nuclear envelope. This membrane separates the contents of the nucleus from the cytoplasm.The envelope helps to maintain the shape of the nucleus and assists in regulating the flow of molecules into and out of the nucleus through nuclear pores.
Chromosomes are also located in the nucleus.
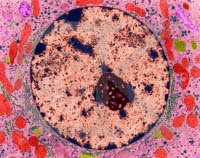 When a cell is "resting" i.e. not dividing, the chromosomes are organized into long entangled structures called chromatin and not into individual chromosomes as we typically think of them.
When a cell is "resting" i.e. not dividing, the chromosomes are organized into long entangled structures called chromatin and not into individual chromosomes as we typically think of them.The Nucleolus:
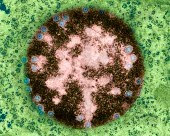 The nucleus also contains the nucleolus which helps to synthesize ribosomes.
The nucleus also contains the nucleolus which helps to synthesize ribosomes.The nucleolus contains nucleolar organizers which are parts of chromosomes with the genes for ribosome synthesis on them. Copious amounts of RNA and proteins can be found in the nucleolus as well.
The nucleus controls the synthesis of proteins in the cytoplasm through the use of messenger RNA. Messenger RNA is produced in the nucleolus of the cell and travels to the cytoplasm through the pores of the nuclear envelope.
This entry was posted on October 4, 2009 at 12:14 pm, and is filed under
biology,
Journey into the Cell
. Follow any responses to this post through RSS. You can leave a response, or trackback from your own site.
Langganan:
Posting Komentar (Atom)

Posting Komentar