Vein
08.47
Diposting oleh Melany Christy
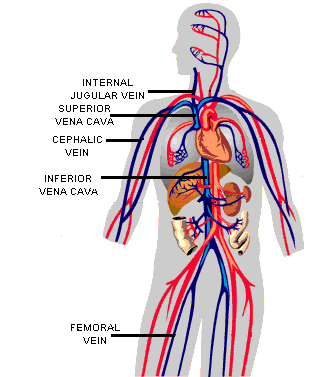
A vein is an elastic blood vessel that transports blood from various regions of the body to the heart. Veins can be categorized into four main types: pulmonary, systemic, superficial, and deep veins.
Pulmonary veins carry oxygenated blood from the lungs to the left atrium of the heart. Systemic veins return deoxygenated blood from the rest of the body to the right atrium of the heart. Superficial veins are located close to the surface of the skin and are not located near a corresponding artery. Deep veins are located deep within muscle tissue and are typically located near a corresponding artery with the same name (for example coronary arteries and veins).
A vein can range in size from 1 millimeter to 1-1.5 centimeters in diameter. The smallest veins in the body are called venules. They receive blood from the arteries via the arterioles and capillaries. The venules branch into larger veins which eventually carry the blood to the largest veins in the body, the vena cava. The blood is then transported from the superior vena cava and inferior vena cava to the right atrium of the heart.
This entry was posted on October 4, 2009 at 12:14 pm, and is filed under
anatomy,
article,
biology
. Follow any responses to this post through RSS. You can leave a response, or trackback from your own site.
Langganan:
Posting Komentar (Atom)

Posting Komentar