The Endoplasmic Reticulum
22.01
Diposting oleh Melany Christy
There are two regions of the ER that differ in both structure and function. One region is called rough ER because it has ribosomes attached to the cytoplasmic side of the membrane. The other region is called smooth ER because it lacks attached ribosomes. Typically, the smooth ER is a tubule network and the rough ER is a series of flattened sacs.
The rough ER manufactures membranes and secretory proteins. In leukocytes (leuk-) the rough ER produces antibodies (anti-). In pancreatic cells the rough ER produces insulin. The rough and smooth ER are usually interconnected and the proteins and membranes made by the rough ER move into the smooth ER to be transferred to other locations.
The smooth ER has a wide range of functions including carbohydrate and lipid synthesis. It serves as a transitional area for vesicles that transport ER products to various destinations. In liver cells the smooth ER produces enzymes that help to detoxify certain compounds. In muscles the smooth ER assists in the contraction of muscle cells and in brain cells it synthesizes male and female hormones.
ribosome
21.23
Diposting oleh Melany Christy
 Ribosomes are organelles that consist of RNA an proteins. They are responsible for assembling the proteins of the cell. Depending on the protein production level of a particular cell, ribosomes may number in the millions.
Ribosomes are organelles that consist of RNA an proteins. They are responsible for assembling the proteins of the cell. Depending on the protein production level of a particular cell, ribosomes may number in the millions.Distinguishing Characteristics:
Ribosomes are typically composed of two subunits: a large subunit and a small subunit. Ribosomal subunits are synthesized by the nucleolus. These two units join together when the ribosome attaches to messenger RNA to produce a protein in the cytoplasm.Location in the Cell:
There are two places that ribosomes usually exist in the cell: suspended in the cytosol and bound to the endoplasmic reticulum. These ribosomes are called free ribosomes and bound ribosomes respectively. In both cases, the ribosomes usually form aggregates called polysomes.Free ribosomes usually make proteins that will function in the cytosol, while bound ribosomes usually make proteins that are exported or included in the cell's membranes. Interestingly enough, free ribosomes and bound ribosomes are interchangeable and the cell can change their numbers according to metabolic needs.
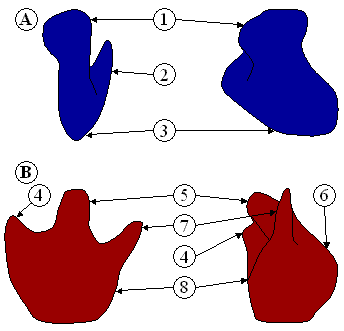 Ribosome structure indicating small subunit (A) and large subunit (B). Side and front view.
Ribosome structure indicating small subunit (A) and large subunit (B). Side and front view.1 Head
2 Platform
3 Base
4 Ridge
5 Central protuberance
6 Back
7 Stalk
A tiny organelle that is the site of protein synthesis (protein translation) in the living cell. Ribosomes are complex, bead-like structures composed of about 40% protein and 60% ribosomal RNA (rRNA). In eukaryotes, ribosomes are made of four strands of RNA and are often attached to the membranes of the endoplasmic reticulum to form rough ER. In prokaryotes, they are made of three strands of RNA and occur free in the cytoplasm.
Eukaryote ribosomes are produced and assembled in the nucleolus. Three of the four strands are produced there, but one is produced outside the nucleolus and transported inside to complete the ribosome assembly. Ribosomal proteins enter the nucleolus and combine with the four strands to create the two subunits that will make up the completed ribosome. The ribosome units leave the nucleus through the nuclear pores and unite once in the cytoplasm. Some ribosomes will remain free-floating in the cytoplasm, creating proteins for the cell's use. Others will attach to the endoplasmic reticulum and produce the proteins that will be "exported" from the cell.
Protein synthesis requires the assistance of two other RNA molecules. Messenger RNA (mRNA) provides instructions from the cellular DNA for building a specific protein. Transfer RNA (tRNA) brings the protein building blocks, amino acids, to the ribosome. Once the protein backbone amino acids are polymerized, the ribosome releases the protein and it is transported to the Golgi apparatus. There, the proteins are completed and released inside or outside the cell. For more details of the role played by ribosomes in protein synthesis, see protein translation.
Mitochondria
21.11
Diposting oleh Melany Christy
Mitochondria are the cell's power producers. They convert energy into forms that are usable by the cell. They are the sites of cellular respiration which ultimately generates fuel for the cell's activities.
What are their distinguishing characteristics?
Mitochondria are bounded by a double membrane. Each of these membranes is a phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins. The outermost membrane is smooth while the inner membrane has many folds. These folds are called cristae. The folds enhance the "productivity" of cellular respiration by increasing the available surface area.
The double membranes divide the mitochondrion into two distinct parts: the intermembrane space and the mitochondrial matrix. The intermembrane space is the narrow part between the two membranes while the mitochondrial matrix is the part enclosed by the innermost membrane. Several of the steps in cellular respiration occur in the matrix due to its high concentration of enzymes.

Mitochondrion with matrix, Image courtesy of The Virtual Cell.
Mitochondria are semiautonomous (semi- auto-) in that they can divide and grow to make more of themselves. They also have their own DNA and ribosomes.
Share your opinions
The Nucleus
21.03
Diposting oleh Melany Christy
 The nucleus is a membrane bound structure that contains the cell's hereditary information and controls the cell's growth and reproduction.
The nucleus is a membrane bound structure that contains the cell's hereditary information and controls the cell's growth and reproduction.It is commonly the most prominent organelle in the cell.
Distinguishing Characteristics:
The nucleus is bounded by a double membrane called the nuclear envelope. This membrane separates the contents of the nucleus from the cytoplasm.The envelope helps to maintain the shape of the nucleus and assists in regulating the flow of molecules into and out of the nucleus through nuclear pores.
Chromosomes are also located in the nucleus.
 When a cell is "resting" i.e. not dividing, the chromosomes are organized into long entangled structures called chromatin and not into individual chromosomes as we typically think of them.
When a cell is "resting" i.e. not dividing, the chromosomes are organized into long entangled structures called chromatin and not into individual chromosomes as we typically think of them.The Nucleolus:
 The nucleus also contains the nucleolus which helps to synthesize ribosomes.
The nucleus also contains the nucleolus which helps to synthesize ribosomes.The nucleolus contains nucleolar organizers which are parts of chromosomes with the genes for ribosome synthesis on them. Copious amounts of RNA and proteins can be found in the nucleolus as well.
The nucleus controls the synthesis of proteins in the cytoplasm through the use of messenger RNA. Messenger RNA is produced in the nucleolus of the cell and travels to the cytoplasm through the pores of the nuclear envelope.
cilia and flagella
21.00
Diposting oleh Melany Christy
 In Journey into the Cell, we looked at the structure of the two major types of cells: prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
In Journey into the Cell, we looked at the structure of the two major types of cells: prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.Now we turn our attention to the "movers" of a eukaryotic cell, cilia and flagella.
What are cilia and flagella?
If the protrusions are short and numerous they are termed cilia. If they are longer and less numerous (usually only one or two) they are termed flagella.
What are some distinguishing characteristics?
The pattern is so named because a ring of nine microtubule "doubles" has in its center two singular microtubules.
This organization allows the sliding of the microtubule doubles against one another to "bend" the cilia or flagella. This type of organization is found in most eukaryotic cilia and flagella.
Where can cilia and flagella be found?
Cilia can be found in areas such as the respiratory and female reproductive tracts.
The Cell-Cell Structure
20.53
Diposting oleh Melany Christy
Eukaryotic Cells and Prokaryotic Cells
There are two primary types of cells: eukaryotic cells and prokaryotic cells. Eukaryotic cells are called so because they have a true nucleus. The nucleus, which houses DNA, is contained within a membrane and separated from other cellular structures. Prokaryotic cells however have no true nucleus. DNA in a prokaryotic cell is not separated from the rest of the cell but coiled up in a region called the nucleoid.As organized in the Three Domain System, prokaryotes include archaeans and bacteria. Eukaryotes include animals, plants, fungi and protists. Typically, eukaryoitc cells are more complex and much larger than prokaryotic cells. On average, prokaryotic cells are about 10 times smaller in diameter than eukaryotic cells.
Eukaryotes grow and reproduce through a process called mitosis. In organisms that also reproduce sexually, the reproductive cells are produced by a type of cell division called meiosis. Most prokaryotes reproduce through a process called binary fission. During binary fission, the single DNA molecule replicates and the original cell is divided into two identical daughter cells.
Both eukaryotic and prokaryotic organisms get the energy they need to grow and maintain normal cellular function through cellular respiration. Cellular respiration has three main stages: glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and electron transport. In eukaryotes, most cellular respiration reactions take place within the mitochondria. In prokaryotes, they occur in the cytoplasm and/or within the cell membrane.
The Cell-Cell Structure
There are also many distinctions between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cell structure. The following table compares the cell structures found in a typical prokaryotic cell to those found in a typical animal eukaryotic cell.Cell Structure Comparison
| Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic Cell Structure | |||
| Cell Structure | Prokaryotic Cell | Typical Animal Eukaryotic Cell | |
| Cell Wall | Yes | No | |
| Centrioles | No | Yes | |
| Chromosomes | One long DNA strand | Many | |
| Cilia or Flagella | Yes, simple | Yes, complex | |
| Endoplasmic Reticulum | No | Yes (some exceptions) | |
| Golgi Complex | No | Yes | |
| Lysosomes | No | Common | |
| Mitochondria | No | Yes | |
| Nucleus | No | Yes | |
| Peroxisomes | No | Common | |
| Cell Membrane | Yes | Yes | |
| Ribosomes | Yes | Yes | |
Osmosis
09.25
Diposting oleh Melany Christy
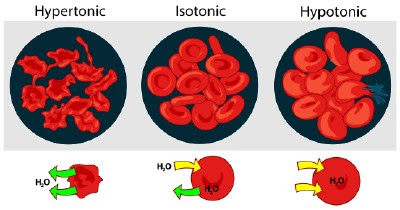
- If the salt water solution is hypertonic it would contain a higher concentration of solute and a lower concentration of water than the blood cells. Fluid would flow from the area of low solute concentration (the blood cells) to an area of high solute concentration (water solution). As a result the blood cells will shrink.
- If the salt water solution is isotonic it would contain the same concentration of solute as the blood cells. Fluid would flow equally between the blood cells and the water solution. As a result the blood cells will remain the same size.
- If the salt water solution is hypotonic it would contain a lower concentration of solute and a higher concentration of water than the blood cells. Fluid would flow from the area of low solute concentration (water solution) to an area of high solute concentration (the blood cells). As a result the blood cells will swell and even burst.
Facilitated Diffusion
09.18
Diposting oleh Melany Christy
 Facilitated diffusion is a type of passive transport that allows substances to cross membranes with the assistance of special transport proteins. Some molecules and ions such as glucose, sodium ions and chloride ions are unable to pass through the lipid bilayer of cell membranes.
Facilitated diffusion is a type of passive transport that allows substances to cross membranes with the assistance of special transport proteins. Some molecules and ions such as glucose, sodium ions and chloride ions are unable to pass through the lipid bilayer of cell membranes.Through the use of ion channel proteins and carrier proteins that are embedded in the cell membrane these substance can be transported into the cell. Ion channel proteins allow specific ions to pass through the protein channel. The ion channels are regulated by the cell and are either open or closed to control the passage of substances into the cell. Carrier proteins bind to specific molecules, change shape and then deposit the molecules across the membrane. Once the transaction is complete the proteins return to their original position.gh the use of ion channel proteins and carrier proteins that are embedded in the cell membrane these substance can be transported into the cell. Ion channel proteins allow specific i
Diffusion and Passive Transport
08.29
Diposting oleh Melany Christy
Diffusion
Passive Transport
As illustrated in the image above: "This cartoon illustrates passive diffusion. The dashed line is intended to indicate a membrane that is permeable to the molecules or ions illustrated as red dots. Initially all of the red dots are within the membrane. As time passes, there is net diffusion of the red dots out of the membrane, following their concentration gradient. When the concentration of red dots is the same inside and outside of the membrane the net diffusion ceases. However, the red dots still diffuse into and out of the membrane, but the rates of the inward and outward diffusion are the same resulting in a net diffusion of O."- Steven Berg
Although the process is spontaneous, the rate of diffusion for different substances is affected by membrane permeability. Since membranes are selectively permeable (only some substances can pass), different molecules will have different rates of diffusion. For instance, water diffuses freely across membranes, an obvious benefit for cells since water is crucial to many cellular processes. Some molecules however must be helped across the cell membrane through a process called facilitated diffusion.
Animal Cells
07.52
Diposting oleh Melany Christy
 Animal cells are eukaryotic cells, or cells with a membrane-bound nucleus. Unlike prokaryotic cells, DNA in animal cells is housed within the nucleus. In addition to having a nucleus, animal cells also contain other membrane-bound organelles, or tiny cellular structures, that carry out specific functions necessary for normal cellular operation. Organelles have a wide range of responsibilities that include everything from producing hormones and enzymes to providing energy for animal cells.
Animal cells are eukaryotic cells, or cells with a membrane-bound nucleus. Unlike prokaryotic cells, DNA in animal cells is housed within the nucleus. In addition to having a nucleus, animal cells also contain other membrane-bound organelles, or tiny cellular structures, that carry out specific functions necessary for normal cellular operation. Organelles have a wide range of responsibilities that include everything from producing hormones and enzymes to providing energy for animal cells.Animal Cells: Structures and Organelles
The following are examples of structures and organelles that can be found in typical animal cells:- Centrioles - organize the assembly of microtubules during cell division.
What are centrioles?
Centrioles are cylindrical structures that are composed of groupings of microtubules arranged in a 9 + 3 pattern. The pattern is so named because a ring of nine microtubule "triplets" are arranged at right angles to one another. Centrioles are found in animal cells and play a role in cell division. Centrioles replicate in interphase stage of mitosis and they help to organize the assembly of microtubules during cell division. Centrioles called "basal bodies" form cilia and flagella.
- Cytoplasm - gel-like substance within the cell.
The cytoplasm is clear in color and has a gel-like appearance. It is composed mainly of water and also contains enzymes, salts, organelles, and various organic molecules. The cytoplasm helps to move materials around the cell and also dissolves cellular waste.
- Endoplasmic Reticulum - extensive network of membranes composed of both regions with ribosomes (rough ER) and regions without ribosomes (smooth ER).
- Golgi Complex - responsible for manufacturing, storing and shipping certain cellular products.
- Lysosomes - sacs of enzymes that digest cellular macromolecules such as nucleic acids.
- Microtubules - hollow rods that function primarily to help support and shape the cell.
- Mitochondria - power producers and the sites of cellular respiration.
- Nucleus - membrane bound structure that contains the cell's hereditary information.
- Nucleolus - structure within the nucleus that helps in the synthesis of ribosomes.
- Nucleopore - tiny hole within the nuclear membrane that allows nucleic acids and proteins to move into and out of the nucleus.
- Ribosomes - consisting of RNA and proteins, ribosomes are responsible for protein assembly.






